Keeping your assets and equipment running at peak performance is critical to any organization. In today’s world, asset and equipment breakdowns and failures still occur. It is essential for companies to have a process in place to track all of their assets and equipment that are prone to failures in order to maximize uptime and keep disruptions at a minimum.
With the proper management of failures, you can reduce the negative impact on your organization. To help you manage these failures, there are a number of important metrics that have been put in place to help you monitor these failures
Some of the industry’s most commonly tracked metrics are MTTR (mean time to repair), MTBF (mean time before failure), and MTTF (mean time to failure). We’ll discuss what each of those acronyms means and how you can use them to improve your operations. Also included are some additional commonly used maintenance metrics to help you get an even better understanding of your maintenance operations performance.

What is Mean Time To Repair (MTTR)
Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) is a Key Performance Indicator (KPI) that represents the average time required to troubleshoot and repair failed equipment and return it to normal operating conditions. MTTR gives organizations a more accurate analysis of how well their teams are responding to repairs and equipment problems.
Taking too long to repair an asset drives up the costs, due to downtime until the new part arrives and the possible window of time required to make the repair. To improve MTTR, many companies purchase spare products so that a replacement can be installed quickly. Generally, customers will inquire about the turn-around time of repairing a product, which affects MTTR.
How is Mean Time To Repair (MTTR) used?
- Internal teams use this metric to keep track of repairs.
How to Calculate Mean Time To Repair (MTTR)
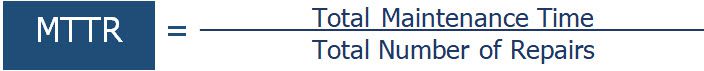
- Total time spent on unplanned maintenance for an asset\equipment.
- Divide that number by the number of repairs.
Example
- A generator has broken down 10 times during the years.
- You spent 100 hours to repair the generator.
- The MTTR is 10.
- You need to determine what MTTR value is acceptable for your organization.
Value of Mean Time To Repair (MTTR
- Viewing historic records to make better decisions on when to repair or replace an asset.
- Gives a snapshot of how quickly the maintenance team responds to failed assets or equipment.
- Gives you a look into how effective and efficient your preventive maintenance program is performing.
Improving Mean Time To Repair (MTTR)
- Keep accurate historic records of repairs and time spent on repairs.
- Document frequently used parts that are needed for repairs.
- Ensure that inventory is well stocked.
- Evaluate the knowledge of the technical staff to determine if additional training or certification is required.
MTTR usually stands for Mean Time To Repair, but it can also represent other metrics that you might want to include in your KPIs.
What is Mean Time To Recovery (MTTR)?
- The average time it takes to recover from an asset or equipment failure.
- Shows how quickly an asset or equipment failure is resolved.
How is Mean Time To Recovery (MTTR) used?
- This is a good metric for assessing the speed of your overall recovery process.
How to Calculate: Mean Time To Recovery (MTTR)
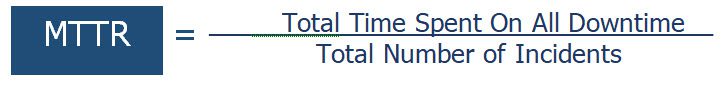
- Total time spent on all of the downtime during a specific period.
- Divide that number by the number of incidents.
What is Mean Time To Respond (MTTR)?
- The average time it takes to recover from an asset or equipment failure from the time of receiving the first failure alert.
How is Mean Time To Respond (MTTR) used?
- This is often used in cybersecurity when measuring a team’s success in neutralizing system attacks.
How to Calculate: Mean Time To Respond (MTTR)
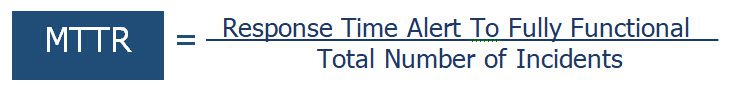
- Total time from alert to when the equipment is fully functional
- Divide that number by the number of incidents.
What is Mean Time To Resolve (MTTR)?
- The average time it takes to resolve an asset or equipment failure from when the cause of the failure is identified and fixed.
- Use this metric comparing it with Mean Time to Recovery. The difference between the two metrics shows how fast the team responded to resolving the failure and making the system more reliable and preventing the past incidents from happening again.
How is Mean Time To Resolve (MTTR) used?
- This is typically used when talking about unplanned incidents, not service requests (which are typically planned).
How to Calculate Mean Time To Resolve (MTTR)

- Total the full resolution time during the period you want to track.
- Divide that number by the number of incidents.
What is Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)?
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) is a KPI that measures equipment reliability and the amount of time that elapses between one failure and the next. These metrics provide detailed and in-depth information on the status of equipment and assets. This KPI helps organizations optimize preventive maintenance schedules to help avoid unexpected failures and unnecessary maintenance. This will let you know the expected life span of an asset. MTBF is commonly used for repairable items. >
How is Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) used?
- Buyers who are looking for the most reliable products.
- Buyers looking for the safest equipment for their plant.
- Internal teams use this metric to identify issues and track successes and failures.
- Metric to inform customers on when they should bring an asset in for maintenance, replace a part or upgrade a system.
How to Calculate Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
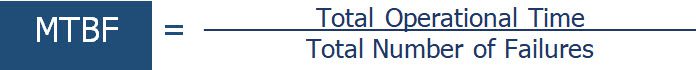
- Identify the total number of operational hours for a specific asset over a defined timeframe.
- Divide that number by the number of failures that happened during that timeframe.
- A low MTBF can be contributed to either an operator error or past repairs that were not satisfactorily made.
Example
- A piece of equipment has been fully operational for 10,000 hours over a period of one year.
- The equipment broke down 10 times during that timeframe.
- The MTBF for this piece of equipment would be 1,000 hours.
Value of Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
- Identify previous issues and repairs.
- Identify issues and repair timeframes so that you can properly schedule preventive maintenance before the failure.
- Improve product quality and reliability.
Improving Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
- Improve preventive maintenance processes.
- Do a root cause analysis and get an understanding of why it failed.
- Look at options, maybe the replacement part needs to be a higher-quality or a different brand.
- Having a more thorough understanding of your asset and making changes can greatly improve MTBF.
Mean Time To Failures (MTTF) is a KPI that measures the reliability for non-repairable equipment. It represents the length of time that an asset is expected to last in operation until it fails. Unlike MTBF which is used for repairable items, MTTF is used when fixing an asset isn’t an option.
How to Calculate Mean Time To Failures (MTTF)
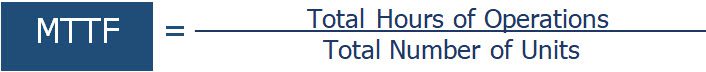
- Take the total number of operational hours and divide that by the number of assets you’re monitoring.
Example
- You have four circulating pumps.
- First circulating pump fails after ten hours.
- Second circulating pump fails after twelve hours.
- Third circulating pump fails after six hours.
- Fourth circulating pump fails after eight hours.
- Total uptime of 36 hours
- Divide the total uptime of 36 hours by the number of circulating pumps (4), which equals nine hours.
- The final calculation is the average lifespan of that particular type and model circulating pump.
- The conclusion is that this specific make and model of circulating pumps will need to be replaced on an average of every nine hours.
Value of Mean Time To Failures (MTTF)
- Shows the reliability of the parts, brand, and model pertaining to an asset or piece of equipment.
Improving Mean Time To Failures (MTTF)
- The best way to improve MTTF is to keep your assets and equipment in good working order.
- Have a good preventive maintenance plan in place.
Tools For Effective Maintenance Management
Metrics are crucial to understanding, diagnosing, and resolving the issues that prevent your maintenance organization from operating at peak efficiency. Each metric provides a different insight into the performance of your maintenance operations. When used together, they can give you a more comprehensive insight into how successful your team is in resolving issues and where the team can improve. Although there are many different types of metrics that can also be valuable, these are the standard metrics tools that are most commonly used and will give you a good understanding of your overall maintenance operations.
- Mean Time to Detection (MTTD) is the average time it takes your team to identify an issue.
- Mean Time to Acknowledge (MTTA) is the average time it takes from when an alert is triggered to when work begins on resolving the issue.
- Mean Time to Respond (MTTR) is the average time it takes to return the asset\equipment to operational condition after receiving notification of the failure.
- Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) is the average time it takes from the detection of an issue until it has been fixed.
- Mean Time to Resolve (MTTR) is the average time from detection of the failure until it is fixed.
- Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR) is the average it takes to recover from a failure.
- Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) is the average time between system breakdowns.
- Mean Time To Failures (MTTF) is the amount of time that elapses between one failure and the next.
- Planned Maintenance Percentage (PPC) is the percentage of time spent on planned maintenance activities against unplanned.
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) measures the productivity of a piece of equipment. This metric provides valuable data on how effective an organization’s maintenance processes are operating based on factors like equipment quality, performance, and availability.
Final Thoughts
eWorkOrders CMMS provides organizations with easy-to-use tools that will help you manage your maintenance operations more efficiently.